Wart Removal Treatment in Navi Mumbai
Warts are benign skin growths caused by a viral infection (human papillomavirus or HPV). They can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the hands, feet, and face. Warts are generally harmless but can be bothersome or unsightly.
Types of Warts
- Common Warts: Raised, rough, and often found on hands or fingers.
- Plantar Warts: Found on the soles of the feet, often causing pain when walking.
- Flat Warts: Smaller, flatter, and often appear in clusters.
- Filiform Warts: Thread-like warts that appear on the face, usually around the mouth or eyes.
- Genital Warts: Occur in the genital area and are transmitted sexually.
- Periungual Warts: Found around or under the nails, can cause nail damage.
Wart Removal Methods
- 1. Over-the-Counter Treatments (OTC)
- Salicylic Acid:
- Most common treatment. It works by dissolving the wart tissue.
- Applied in liquid or patch form and should be used regularly (typically over weeks).
- Best for common and plantar warts.
- Side effects: Skin irritation around the wart.
- Cryotherapy (Home Freezing Kits):
- OTC products that use liquid nitrogen or similar agents to freeze the wart.
- Used on smaller warts and can be effective when used consistently.
- Best for: Smaller, less stubborn warts.
- Salicylic Acid:
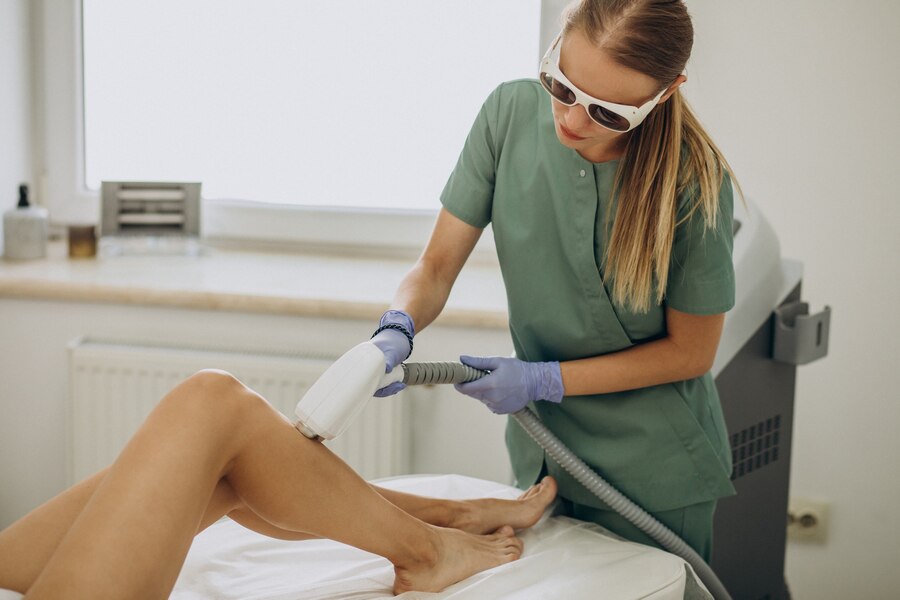
- 2. Cryotherapy (In-Office Treatment)
- Cryotherapy performed by a healthcare professional involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen.
- The cold temperature destroys the wart tissue, causing it to fall off.
- Typically requires multiple sessions (1-2 weeks apart).
- Best for: Larger or stubborn warts, like plantar warts.
- 3. Laser Treatment
- Uses a focused laser beam to burn and destroy the wart tissue.
- Can be very effective for wart removal and is typically used for more difficult warts.
- Laser treatment is minimal pain with quick recovery.
- Best for: Warts that don’t respond to other treatments or warts in sensitive areas.
- 4. Electrosurgery (Electrodesiccation)
- A technique that uses electric currents to burn the wart tissue.
- It’s effective for removing stubborn warts.
- Often requires local anesthesia due to the heat.
- Best for: Large or deeply-rooted warts that resist other methods.
- 5. Minor Surgery
- Involves cutting out the wart or scraping it off.
- Performed under local anesthesia and can be done in a doctor's office.
- This method may leave a scar and requires aftercare to prevent infection.
- Best for: Large or persistent warts that don't respond to other treatments.
- 6. Cantharidin
- Cantharidin is a blistering agent applied to the wart. It causes a blister to form underneath the wart, lifting it off the skin.
- This is usually followed by removal of the wart once the blistering process is complete (in about 1-2 weeks).
- Best for: Smaller warts, like common warts or warts on the hands.
- 7. Immunotherapy
- Topical Immunotherapy: Treatments like Imiquimod cream stimulate the body's immune system to target and fight the wart.
- This is typically used for difficult-to-treat warts like genital warts or plantar warts.
- Requires regular application over several weeks.
- Best for: Stubborn warts that haven’t responded to other treatments.
- 8. Home Remedies (Natural Treatments)
- Duct tape: Some people find that covering the wart with duct tape for several days can help remove it over time.
- Apple cider vinegar: Soak a cotton ball in vinegar and apply it to the wart, then cover with a bandage overnight.
- Garlic: Garlic contains antiviral properties, and applying it to a wart may help it fade.
- Note: While these remedies are popular, their effectiveness is not scientifically proven, and they can be slow or ineffective. Always consult a healthcare professional for the most reliable options.
What to Expect During Wart Removal
- Treatment Process:
- For most treatments, the wart will either shrink, change color, or scab over as it heals.
- Some methods (like cryotherapy or laser) may cause mild discomfort.
- If a surgical method is used, there may be local anesthesia to minimize pain.
- Healing Time:
- Depending on the treatment, healing time can vary.
- For minor methods (like cryotherapy or OTC treatments), the wart should fall off in about 2-3 weeks.
- Surgical methods may require several weeks for full recovery.
Aftercare Tips
- Keep the area clean and dry to prevent infection.
- Avoid scratching or picking at the treated wart.
- Apply moisturizing ointment or antibiotic cream if instructed.
- For cryotherapy or laser treatments, you may have a blister or scab, so be sure to protect the area from friction.
- Follow any specific aftercare instructions given by your healthcare provider to promote healing.
When to See a Doctor
- If warts are painful, changing in appearance, or spreading rapidly.
- If over-the-counter treatments have failed to work after a few weeks.
- If the wart is located in a sensitive area like the face or genital area.
- If you have large, stubborn, or recurrent warts.
Final Thoughts
- Warts are generally harmless, but if they’re bothersome or persistent, there are multiple treatments available.
- Cryotherapy and laser treatments are often the most effective for most types of warts.
- Always follow aftercare instructions carefully to avoid recurrence or complications.